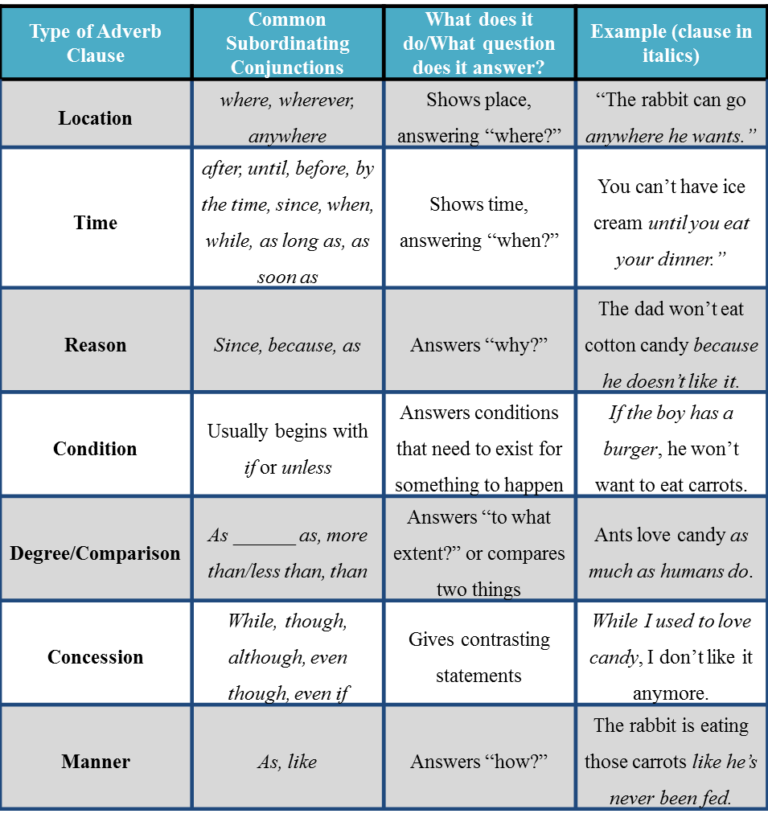
A noun clause, like other clauses, is a group of words that includeS a subject and a verb. As a dependent clause, it must be connected to an independent clause to form a complete sentence. A noun clause functions as a noun, which means it can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, object of a preposition, predicate nominative, or appositive. One point to bear in mind is a noun clause is not a noun modifier. Noun clauses are clauses that function as nouns. They are noun clauses, adjective clauses, and adverbial clauses.

Definitions and examples of noun clauses in sentences. Remember that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. You now know that noun clauses can be used a subjects, direct objects, objects of prepositions, and complements in sentences. Noun clauses often follow certain phrases.

We also introduce them with certain words or markers. The word order in a noun clause is always the normal order of subject + verb, even if the noun clause begins with a question word. The download will give you more opportunities to practice understanding and using noun clauses. In linguistics, a dependent clause is a clause that augments an independent clause with additional information, but which cannot stand alone as a sentence.

Dependent clauses either modify the independent clause of a sentence or serve as a component of it. Some grammarians use the term subordinate clause as a synonym for dependent clause. Others use subordinate clause to refer only to adverbial dependent clauses. The different types of dependent clauses include noun clauses, relative clauses, and adverbial clauses. Having trouble finding the subject or object in a sentence? This is also important if you're in university or taking a test like IELTS or TOEFL.

As a writer, I focus my attention on the many elements we use to build great sentences and paragraphs. I've broken down this advanced part of English grammar and will teach it to you simply—so you can understand and use the noun clauses in your own writing. I'll show you many examples of noun clauses, so you can see the noun clause in context.

Take the quiz to practice identifying the types of noun clauses in example sentences. A noun clause is a clause that functions as a noun. They cannot stand alone and need to be part of an independent clause to form a complete sentence. Noun clauses can be used in the same way as nouns. This means they can be subjects, objects, or complements in a sentence. A noun clause refers to a clause that serves the same purpose as a noun and is usually dependent.

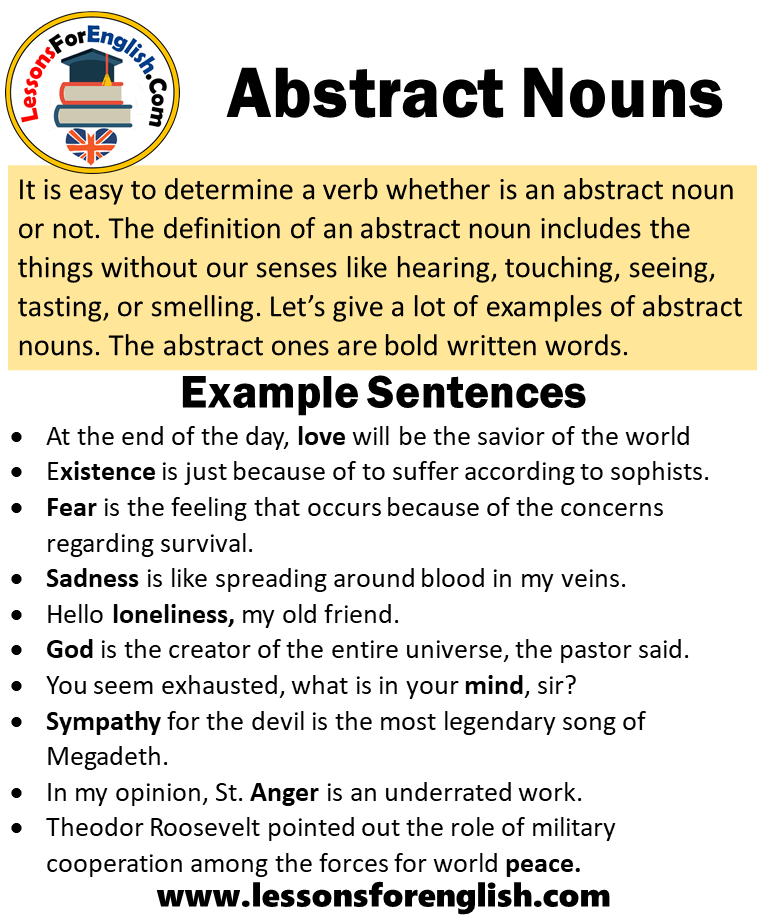
Just like nouns do, a noun clause names people, things, places, and ideas. Noun clauses typically have a verb and a subject, but they cannot express a complete thought in a sentence; hence they are known as dependent clauses. Since noun clauses cannot form complete sentences, they are usually used together with an independent clause. This article gives in-depth insights on noun clauses and the examples of noun clauses. In this example the subject of the clause is i and the verb is see i know that patience has its limits.

A noun clause cannot stand alone because it is not a complete thought. Nouns can function as subjects direct objects indirect objects object of the preposition and predicate nominatives. Noun clauses are a type of dependent clause that perform nominal functions. In grammar, a subject is a word, phrase, or clause that performs the action of or acts upon the verb.

In addition to nouns and pronouns, noun clauses also perform the grammatical function of subject. A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun. Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Noun clauses can act as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, predicate nominatives, or objects of a preposition.
The subordinators do the work of connecting the dependent clause to another clause to complete the sentence. In each of the dependent clauses, the first word is a subordinator. Subordinators include relative pronouns, subordinating conjunctions, and noun clause markers. Whatever happens to her is none of my business.

Noun clauses can act as subjects direct objects indirect objects predicate nominatives or objects of a preposition. Like all clauses a noun clause has a subject and a verb. The noun clause is a clause that functions like a noun in the sentence. Nouns can function as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, object of the preposition, and predicate nominatives. The bolded noun clauses are dependent clauses.

Unlike independent clauses, they can't stand alone as full sentences. Noun clauses function to add more details to a sentence. If you're not sure whether a clause is a noun clause, try replacing it with other nouns or pronouns. Look for a question word to link the clauses. Most of the time, noun clauses start with a question word, sometimes called a subordinating word.

The word can either be a relative pronoun, which acts as a noun, or a subordinating conjunction that introduces a dependent clause. This word links the 2 clauses together and addresses a question from the independent clause. A dependent, or subordinate, clause contains a subject and a verb or verb phrase but does not express a complete thought. As a result, it cannot stand alone as a sentence. Dependent clauses can function either as noun clauses, adjective clauses, or adverb clauses. Some grammars use the term nominal clause for noun clauses.

Most people are comfortable with the idea of a noun, but they may not feel so confident when it comes to the noun clause. A noun clause is a group of words acting together as a noun. These clauses are always dependent clauses. That is, they do not form a complete sentence.

Take a look at some sample sentences containing noun clauses to understand their purpose and function. Subordinate or dependent clauses refer to the type of clauses that depend on an independent clause to express a complete meaning and cannot stand alone as a sentence. These clauses start with a dependent word like a relative pronoun or a subordinate conjunction. Such as, who, because, and, but, although, where, when, etc. However, it cannot stand alone as a sentence. The most common word among them is that.

Examples of noun clause showed here in bold. A noun clause, like other clauses, is a group of words that includes a subject and a verb. The underline words are noun clauses and form parts of the sentences and . I'm elizabeth o'brien, and my goal is to get you jazzed. Clauses are groups of words that have both subjects and predicates. Unlike phrases, a clause can sometimes act as a sentence – this type of clause is called an independent clause.

While the independent clause could be used by itself as a complete sentence, the subordinate clause could not. It cannot function on its own because it leaves an idea or thought unfinished. These help the independent clauses complete the sentence. Alone, it cannot form a complete sentence.
This post has considered one of the major sub-types of the subordinate clause or the dependent clause, the noun clause with its types, functions and examples. Ensure you check the two other sub-types, the adverbial clause and the relative clause. Do not forget to check the post, what is a clause as it would help you put all the sub-types in perspective.

Remember to share this post and others with your friends by using our Social Media share buttons. Conjunctions are "words that link words, phrases, and clauses." A subordinating conjunction is a conjunction that introduces a subordinate or dependent clause. Subordinating conjunctions that introduce noun clauses are also referred to as noun clause markers. The subordinating conjunctions in English that introduce noun clauses are that , if, whether, wh- words, wh-ever words, and sometimes for.

The term "noun clause" might sound confusing, but finding and identifying one is much easier than you might think. Simply put, a noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of a noun in the sentence. A dependent clause is a phrase that can't stand on its own as a complete sentence. If a dependent clause can stand in for a person, place, or thing, then it's a noun clause. By breaking down the sentence into simpler parts, you can find noun clauses easily. With a bit more work, you can identify the 5 types of noun clauses and how they operate in a sentence.

A conjunction is a word that joins other words, phrases, or clauses. Subordinate conjunctions join dependent clauses to independent clauses. Some common subordinate conjunctions are after, although, as, as if, because, before, if, since, so that, than, unless, until, when, where, and while. A noun serves as the subject of the verb in a sentence or it serves as the complement of the verb in a sentence; so does a noun clause and even a nominal or noun phrase. Not all sentences have a dependent clause.

Simple sentences like "I went to school" only have an independent clause. Complex sentences, which have 1 independent clause and at least 1 dependent clause, can contain noun clauses. These nominal clauses are examples of dependent clauses—in contrast to independent clauses, those clauses that function as complete sentences." A noun clause serves a similar role as a noun.

To quickly identify a noun clause in a sentence, one can look for words like whoever, why, whatever, whichever, what, how, and many more. A noun clause can either act as a subject or an object. Objects include; prepositional objects, indirect objects, and direct objects. Noun clauses function in any way that a one-word noun can function. They are great additions to a sentence when you want to provide more information and vary your sentence structure.

Compare noun clauses to different types of clauses with a guide to teaching adverbial and adjective clauses. A noun phrase, or nominal , is a phrase that has a noun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions.

Nouns are basic to sentence structure because they, along with pronouns, provide the subject of the sentence. In addition, a noun functions as a direct object of a verb, an indirect object of a verb, object of a preposition, or a complement. The subject can be a person, place, thing or idea. What is the function of noun clause in a sentence? A noun clause functions as a noun in a sentence. It follows a linking or copular verb to describe or modify the subject of the sentence.

Unlike noun phrases, noun clauses contain both a subject and a verb. The sixth grammatical function that noun clauses perform is the prepositional complement. A prepositional complement is a word, phrase, or clause that directly follows a preposition and completes the meaning of the prepositional phrase. By the Arab grammarians every clause beginning with an independent subject is regarded as a noun-clause, and every clause beginning with a finite verb as verbal.

All the simple sentences above are independent clauses because all have complete meanings and stand alone as sentences. The nonfinite, or unconjugated, verbs in the noun clauses are to wash , to come , reciting , singing , and eat . Notice also that the object pronouns function as the subject of the nonfinite noun clause when the verb is an infinitive or present participle. Similar to the prepositions, each of these sentences could be complete before the conjunctions . The adjective complement provides further detail.
Besides, in each of these examples, these adjective complements are noun clauses. Use a semicolon between two independent clauses that are connected by conjunctive adverbs or transitional phrases. A clause is a group of words containing a subject and a verb. A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, or idea. In this posting I talk about how to form and correctly use noun clauses.

The download at the end will give you additional practice using noun clauses. The noun clause is acting as the direct object of the sentence. In the noun clause "you said" is a subject plus a verb. However, "what you said yesterday" cannot stand alone and therefore must be paired with an independent clause. In this pair of examples, we have two clauses to look at. In example we have a noun clause functioning as a direct object, and a noun clause that is a subject.

In example , the first clause is an adjective clause modifying 'cousin', and the second clause is an adverb clause modifying 'applying'. For changing noun clauses into noun phrases we have to remove the subject and change the verb into infinitive phrases or gerund phrases. In all the options the subject is not present then we have to look at the verb part. If we choose option A then it is a noun phrase but this does not completely change the meaning. A subject complement is a word, phrase, or clause that follows a copular, or linking, verb and describes the subject of a clause.











































